Quick Overview
Steam systems demand far more from valves than standard water or gas lines. High temperature, pressure fluctuation, thermal shock and condensate all place extreme stress on valve components. At Vcore Valve, we work with steam valves every day across power plants, chemical processing and HVAC networks. This guide explains the main types of valves used in steam applications, how they work, where they perform best, and how to select the right valve for long-term safety and efficiency.
Opening Scenario: A Familiar Steam System Problem
“Why does this valve fail every year?”
We hear this question often from plant engineers. In most cases, the failure isn’t the steam itself—it’s the wrong valve type installed in the wrong location. Steam does not forgive design shortcuts.
User Pain Points
1. High Failure Rates in Steam Lines
Standard valves not designed for steam often suffer seat erosion, leakage or stem seizure.
2. Confusion Between Control and Isolation Valves
Many buyers assume any valve can regulate steam flow—this leads to unstable operation and energy loss.
3. Safety Risks Under Pressure
Improper valve selection can result in overpressure, water hammer or catastrophic equipment damage.
Solutions & Expert Recommendations
1. Use Steam-Rated Valve Designs Only
Steam applications require materials, sealing structures and tolerances engineered specifically for high temperature service.
2. Separate Isolation, Control and Protection Functions
Each function in a steam system should be handled by a dedicated valve type.
3. Choose Proven Manufacturing Standards
At Vcore Valve, all steam valves undergo pressure testing, thermal cycling simulation and material verification before delivery.
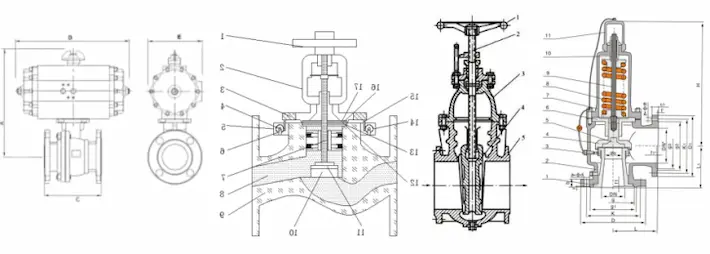
Main Types of Valves Used in Steam Applications
Steam systems rely on multiple valve types, each with a defined role.
Steam Globe Valve
Designed for throttling and precise flow control. The disc-and-seat structure allows stable regulation under pressure.
Steam Gate Valve
Used for full open or full close service only. Provides minimal pressure drop when fully open.
Steam Ball Valve
Suitable for fast isolation. High-performance metal-seated ball valves handle saturated and superheated steam effectively.
Steam Check Valve
Prevents reverse flow and protects equipment such as boilers and turbines.
Steam Control Valve
Automatically regulates steam flow based on temperature or pressure signals.
Steam Safety Valve
Critical protection device that releases excess pressure to prevent system failure.
Case Studies from Vcore Valve
Case 1: Power Plant Isolation Upgrade Replacing standard gate valves with steam-rated forged steel gate valves reduced leakage incidents by 70%.
Case 2: Process Heating Line
Switching from ball valves to globe control valves improved temperature stability and reduced steam consumption.
Data & Technical Comparison
| Valve Type | Primary Function | Temperature Resistance | Pressure Control |
|---|---|---|---|
| Steam Globe Valve | Throttling | Excellent | High |
| Steam Gate Valve | Isolation | Excellent | Low |
| Steam Ball Valve | Fast Shut-off | Good–Excellent | Medium |
| Steam Check Valve | Backflow Prevention | Excellent | Automatic |
| Steam Safety Valve | Pressure Relief | Excellent | Emergency |
Industry Trends & Market Insights
-
Growing demand for forged steel steam valves
-
Increased use of metal-seated ball valves in high-temperature service
-
Strong preference for EN, ASME and ISO certified steam valves
-
Energy efficiency regulations driving better steam control accuracy
Usage & Selection Tips
-
Avoid throttling with gate valves
-
Install check valves near boilers and pumps
-
Use globe or control valves for flow regulation
-
Confirm pressure-temperature ratings carefully
-
Always account for condensate and thermal expansion
Conclusion
Steam is one of the most demanding media in industrial systems, and valve selection directly affects safety, efficiency and operating costs. Understanding the types of valves used in steam applications allows engineers and buyers to design systems that last—not systems that constantly need repair.
At Vcore Valve, we engineer steam valves for real-world conditions, not catalogue assumptions.
FAQ
Q1: What is the best valve for steam flow control?
Globe valves and control valves are best suited for precise steam regulation.
Q2: Can ball valves be used for steam?
Yes, provided they are steam-rated and use metal seats.
Q3: Why are gate valves not used for throttling steam?
Partial opening causes seat erosion and unstable flow.
Q4: Are safety valves mandatory in steam systems?
Yes. They are critical for pressure protection and compliance.
Q5: How often should steam valves be inspected?
Inspection frequency depends on service severity, but annual checks are recommended.