Quick Summary
The anti blowout stems is one of the most important yet often overlooked safety features in industrial ball valves. When system pressure rises unexpectedly, a poorly designed stem can eject from the valve body—posing serious safety risks to personnel and equipment. At Vcore Valve, we consider the ball valve anti blowout stem a non-negotiable design element, not an optional upgrade. This article explains how anti-blowout stems work, why they matter, and how to identify compliant designs with confidence.
A Real-World Engineering Moment
“The valve was closed… then the stem came out.”
This sentence usually appears in incident reports, never in design specifications. Stem blowout incidents are rare—but when they happen, they are violent, dangerous, and entirely preventable with the right ball valve stem design.
Common User Pain Points
Lack of Awareness
Many buyers focus on body material and pressure class, ignoring internal safety features like the anti blowout stem.
Difficulty Identifying True Anti-Blowout Designs
Some valves are marketed as “anti-blowout” without meeting recognised design principles or standards.
Safety Compliance Pressure
Oil & gas and chemical projects increasingly require documented proof of ball valve safety features.
Practical Solutions from Vcore Valve
Choose Internal-Mounted Stem Designs
A true anti blowout stem ball valve uses a stem installed from inside the valve body, physically preventing ejection under pressure.
Verify Compliance with Recognised Standards
Standards such as API ball valve specifications and fire-safe requirements clearly define acceptable stem retention principles.
Select the Right Valve Type
Both floating ball valves and trunnion mounted ball valves can feature anti-blowout stems—but design execution matters more than valve type.
Real Application Case Studies
Case 1: Refinery Isolation Valve
A refinery specified fire safe ball valves with internal anti-blowout stems for hydrocarbon service.
Outcome: Passed safety audit with zero stem-related findings during inspection.
Case 2: Chemical Processing Line
An older valve without an anti-blowout stem experienced stem movement under pressure cycling.
Outcome: Valve replaced with a forged steel ball valve featuring an internal stem retention shoulder, eliminating risk.
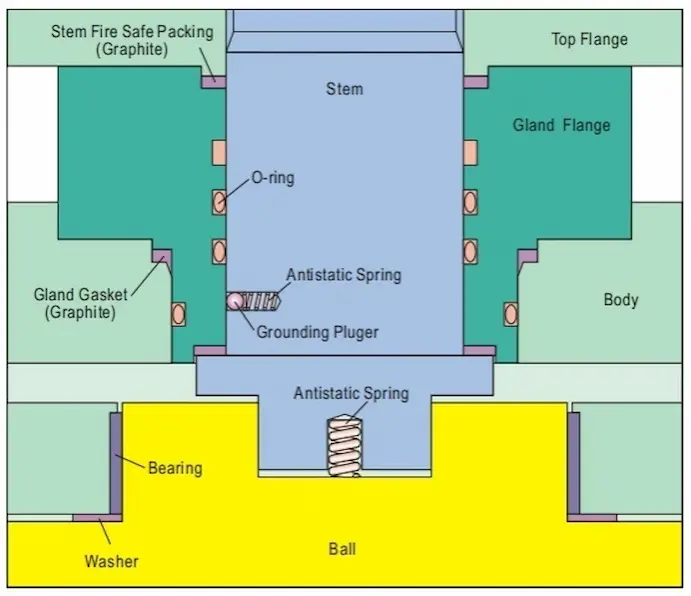
Technical Analysis: How Anti-Blowout Stems Work
In a standard ball valve, system pressure acts upward on the stem. Without retention, excessive pressure or seal failure can force the stem out.
Anti-Blowout Stem Design Logic
-
Stem inserted from inside the valve body
-
Stem shoulder larger than stem bore
-
Pressure pushes stem into the body, not out
Comparison: Anti-Blowout vs Conventional Stem
| Feature | Anti-Blowout Stem | Conventional Stem |
|---|---|---|
| Stem installation | Internal | External |
| Ejection risk | Eliminated | Possible |
| Safety level | High | Limited |
| Compliance | API / fire-safe ready | Often non-compliant |
Engineering tests show internal stem retention can withstand pressures well beyond normal operating limits.
Safety Data and Risk Perspective
Industry safety reviews indicate that stem-related failures, while infrequent, account for:
-
High-energy fluid release incidents
-
Serious operator injury risks
-
Secondary equipment damage
In critical service, a properly designed ball valve anti blowout stem is a basic safety requirement—not a premium feature.
Industry Trends and Market Insight
-
Anti-blowout stems are now standard in most API ball valves
-
EPC contractors increasingly reject valves without documented stem retention design
-
Fire-safe certifications indirectly enforce anti-blowout stem requirements
At Vcore Valve, all industrial ball valves are designed with internal stem retention as standard practice.
Selection and Usage Recommendations
-
Always request stem design confirmation during quotation
-
Review valve cross-section drawings, not just datasheets
-
Combine anti-blowout stems with fire-safe and anti-static features
-
Avoid low-cost valves with unclear stem construction
Conlusion
The anti blowout stem is a small component with enormous safety implications. Choosing a ball valve without this feature exposes systems and people to unnecessary risk.
If you’re specifying industrial ball valves for demanding applications, Vcore Valve delivers proven designs with built-in safety—engineered, tested, and documented.
👉 Contact Vcore Valve today to discuss safer ball valve solutions for your project.
FAQs
What is an anti-blowout stem in a ball valve?
It is a stem designed to prevent ejection under pressure by being retained internally.
Are anti-blowout stems mandatory?
They are required or strongly recommended in most oil & gas and fire-safe applications.
Can floating ball valves have anti-blowout stems?
Yes. Both floating and trunnion designs can include them.
How can I identify a true anti-blowout stem?
Check cross-section drawings and confirm internal stem installation.
Does API require anti-blowout stems?
API standards effectively mandate stem retention through design requirements.
Does Vcore Valve include this feature as standard?
Yes. All Vcore Valve ball valves use anti-blowout stem designs.
References
-
American Petroleum Institute – API 6D: Pipeline Valves
-
API 607 – Fire Test for Quarter-Turn Valves
-
ASME B16.34 – Valves: Pressure–Temperature Ratings
-
ISO 17292 – Metal Ball Valves for Petroleum Industries
-
Valve Manufacturers Association (VMA) – Valve Safety Guidelines
-
Engineering Toolbox – Valve Stem Design Principles
-
Vcore Valve Technical Library – Ball Valve Safety Features