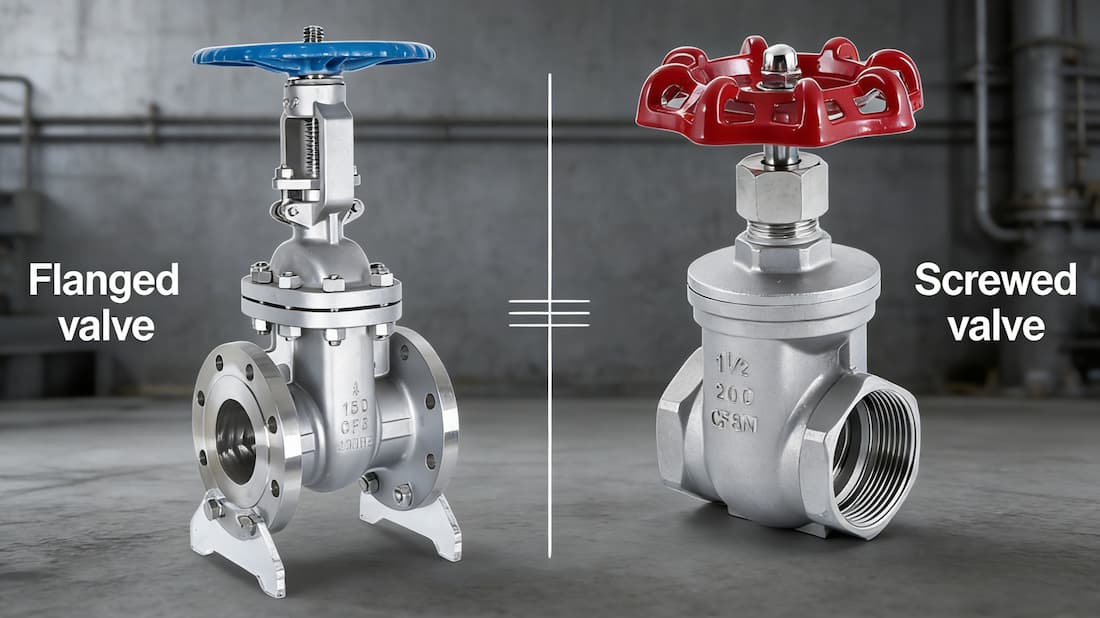
Quick overview
Flanged valves and Screwed valves are two of the most common valve types used in industrial applications. Both have distinct design features, applications, and installation requirements. Choosing the right valve type can improve system efficiency and reduce long-term maintenance costs. This article will explore the differences between these two valve types, helping you make the right choice for your application.
Opening Scenario
Imagine you are sourcing valves for a chemical plant. The engineering team asks, “Should we go for Flanged valves or Screwed valves?” The decision may seem straightforward, but making the wrong choice could lead to frequent maintenance, downtime, or worse, catastrophic failure. How do you decide?
User Pain Points
Difficulty in Choosing Between Flanged Valves and Screwed Valves
Valves aren’t just a matter of brand or price. The choice between Flanged and Screwed valves depends on several critical factors like pressure, temperature, and the medium in question. Many customers lack a deep understanding of valve specifications and make suboptimal choices, leading to operational headaches and unexpected costs.
Ignoring Long-Term Costs
Customers often focus on short-term purchasing costs but overlook long-term factors such as installation complexity, maintenance, and the risk of failures. In high-pressure or corrosive environments, making the wrong choice can lead to expensive repairs and replacement.
The Risk of Incorrect Valve Selection
Using the wrong valve type in inappropriate conditions can lead to leaks, equipment failure, or even dangerous situations. Mismatching valve designs and working conditions is a common mistake that can cause safety hazards and operational inefficiencies.
Solutions and Practical Recommendations
Understand the Characteristics of Flanged Valves and Screwed Valves
-
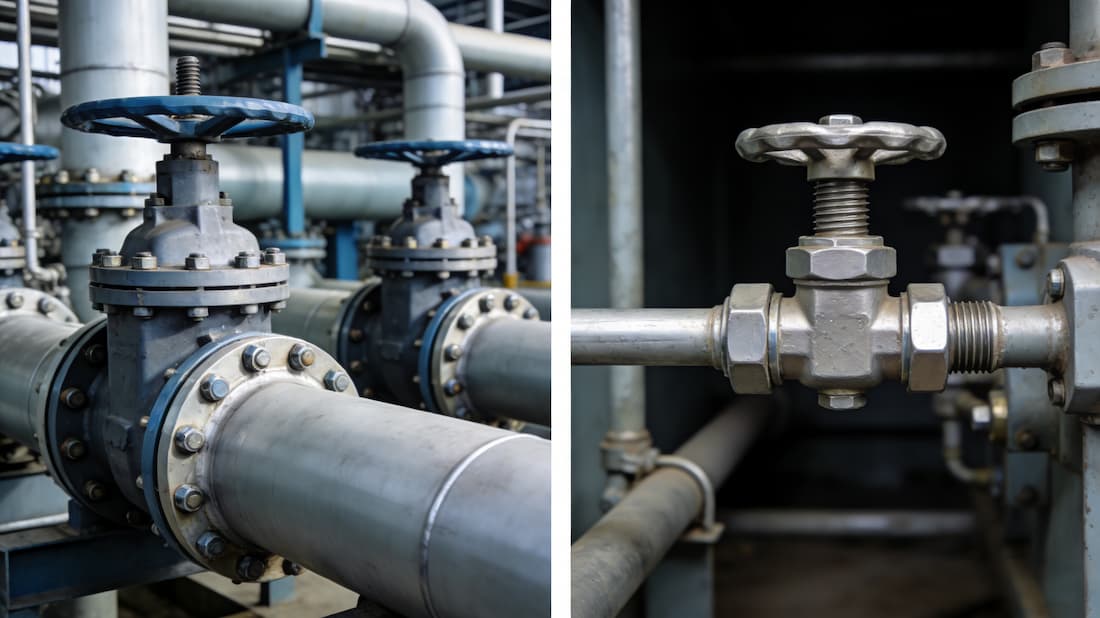
Flanged Valves: Ideal for high-pressure, corrosive environments. Their flanged connection ensures superior sealing, making them suitable for demanding applications. Flanged gate valves are widely used in high-pressure, high-temperature, or corrosive environments due to their superior sealing properties. For more detailed information on flanged gate valves, check out our guide on Gate Valve: 5 Types, Parts, and Working Principle, which provides insights into their design, parts, and working principles.
-
Screwed Valves: Better for lower pressure and moderate temperature environments. Their screw-threaded connection makes them easy to install, but they may not perform as well under extreme conditions.
Match Valve Types to Service Conditions
-
For high-temperature, high-pressure, or corrosive environments, Flanged valves are the best choice. For environments that demand high durability, flanged butterfly valves are a great option, offering reliability and robust sealing. If you’re unsure about sizing, you can explore our Flange Butterfly Valve Sizing Guide for detailed recommendations on choosing the right valve for your needs.
-
For moderate pressure or low-temperature applications, Screwed valves are more cost-effective and easier to install.
Choose the Correct Valve Design
Valve design is just as crucial as material selection. The wrong design can lead to poor sealing, ineffective flow control, or installation difficulties. Always select a valve design that fits your piping layout and operational requirements.
Case Examples
Case 1: Chemical Plant Using Flanged Valves
A chemical plant dealing with corrosive acids replaced their outdated Screwed valves with Flanged valves. This change reduced leaks by more than 50%, enhanced overall reliability, and significantly lowered maintenance costs over the next year.
Case 2: Marine Platform Using Screwed Valves
A marine platform using Screwed valves for its seawater cooling system faced fewer installation issues and lower costs compared to Flanged alternatives. The valves operated smoothly in the medium-pressure environment, avoiding unnecessary maintenance costs.
Data, Scientific Comparison, and Material Analysis
| Feature | Flanged Valves | Screwed Valves |
|---|---|---|
| Pressure Rating | High | Medium to Low |
| Temperature Tolerance | High | Medium |
| Installation Ease | Complex, requires welding | Easy, screw connection |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Sealing Ability | Excellent | Moderate |
| Corrosion Resistance | Strong | Moderate |
Market Trends and Industry Insights
The demand for Flanged valves has risen in industries requiring high corrosion resistance and reliability, such as chemical processing and water treatment. Screwed valves, however, remain in high demand for general use, owing to their lower cost and ease of installation.
Usage and Selection Tips
-
Flanged Valves: Best for high-pressure, high-temperature, and corrosive environments. Always consider the working pressure and temperature before choosing.
-
Screwed Valves: Suitable for lower-pressure environments with relatively mild service conditions. They are ideal for budget-conscious projects where installation simplicity is key.
Summary and Call to Action
Choosing the right valve type is crucial for system efficiency and long-term reliability. Flanged valves and Screwed valves each have their advantages, and understanding your operational requirements is key to making the best choice. For expert assistance in valve selection, contact Vcore engineering team today for customized solutions.
FAQ
Q1: What is a Flanged valve?
A Flanged valve is a type of valve that uses flanged connections for installation. This provides a robust, leak-free seal, making them ideal for high-pressure and corrosive environments.
Q2: What is a Screwed valve?
A Screwed valve uses a threaded connection, which makes it easy to install. It is commonly used in applications with moderate pressure and temperature requirements.
Q3: When should I use Flanged valves?
Flanged valves should be used in high-pressure, high-temperature, or corrosive environments where a strong seal is required for safety and reliability.
Q4: When should I use Screwed valves?
Screwed valves are suitable for applications with moderate pressure and temperature, especially where ease of installation and lower cost are priorities.
Q5: What are the advantages of Flanged valves?
Flanged valves offer superior sealing, making them ideal for demanding environments. They also have better corrosion resistance and can handle higher pressures compared to Screwed valves.
Q6: What are the advantages of Screwed valves?
Screwed valves are cost-effective, easy to install, and best suited for lower-pressure applications. They provide a good solution for systems that do not require high-pressure tolerance.
Q7: Can I use Screwed valves in high-pressure applications?
No, Screwed valves are generally not recommended for high-pressure applications, as their threaded connection may not provide the necessary sealing strength for such conditions.
References
-
ASME B16.5 – Pipe Flanges and Flanged Fittings
Defines the dimensions, materials, and design requirements for pipe flanges and flanged fittings. This standard is critical for understanding the design specifications for flanged valves used in industrial applications. -
ANSI/ASME B16.11 – Forged Fittings, Socket-Welding, and Threaded
Provides the dimensional and technical requirements for threaded fittings, commonly used in screwed valve systems. This standard is essential for designing reliable and safe threaded connections in piping systems. -
Valve World Magazine – Flanged vs Screwed Valves: Advantages and Applications
Discusses the advantages and disadvantages of flanged and screwed valves, including practical insights into their applications in different industrial sectors. -
The Engineering Toolbox – Types of Valves and Their Applications
Provides detailed information on the types of valves, including flanged and screwed, and their common uses in industrial settings, helping engineers choose the right valve for specific applications.