Quick Summary
In this article, we will explore the different types of 3-way valves, their applications, and how they perform in various industrial environments. By understanding the key differences between these valves, you can make informed decisions about which is best suited for your operational needs. Whether you’re working in chemical processing, water treatment, or other industrial sectors, understanding valve types is crucial for optimal performance.
Opening Scenario
Imagine you are overseeing a large industrial plant that handles various chemicals. One of your biggest concerns is the control and direction of flow in your piping system. A 3-way valve is essential in such a system, allowing you to divert or mix flows based on process requirements. But how do you choose the right type of 3-way valve?
User Pain Points
-
Valve Selection Confusion
Choosing the right 3-way valve can be overwhelming due to the wide variety of options. With multiple valve types designed for different applications, it’s often unclear which one offers the best solution for specific needs. -
Performance vs. Cost Dilemma
Many businesses face the dilemma of balancing valve performance with budget constraints. While high-performance 3-way valves offer greater durability and reliability, they come with a higher initial cost, leading to hesitation in selecting the best product. -
Lack of Technical Expertise
Inadequate technical knowledge can lead to poor decision-making. Without a clear understanding of core features such as material compatibility, flow control capabilities, and installation requirements, businesses often end up selecting a valve that underperforms.
Solutions & Recommendations
-
Understand Valve Types
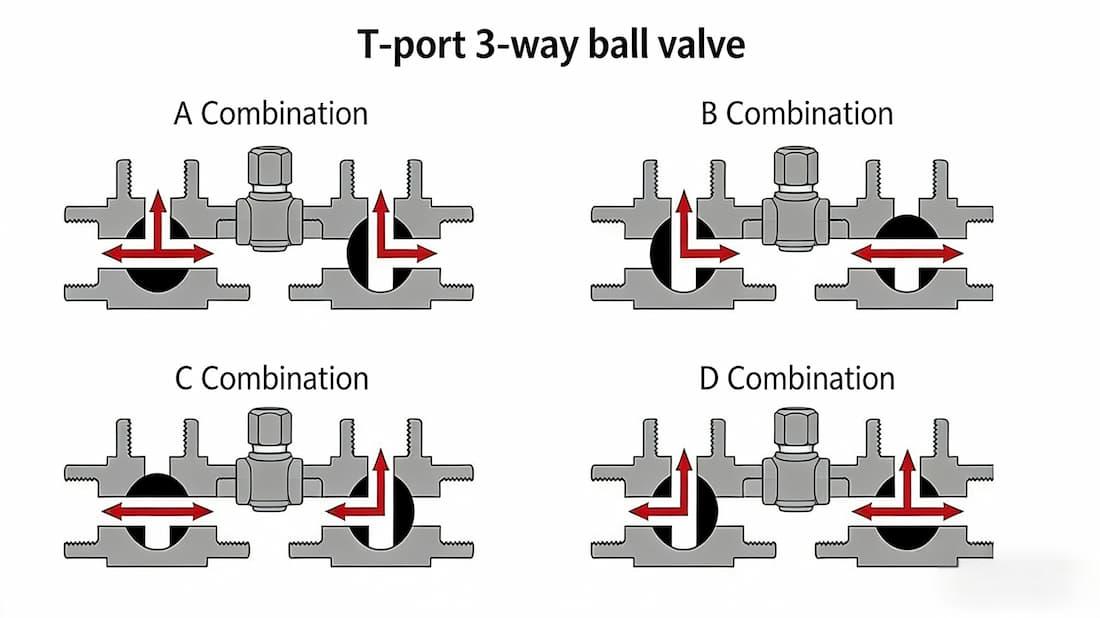
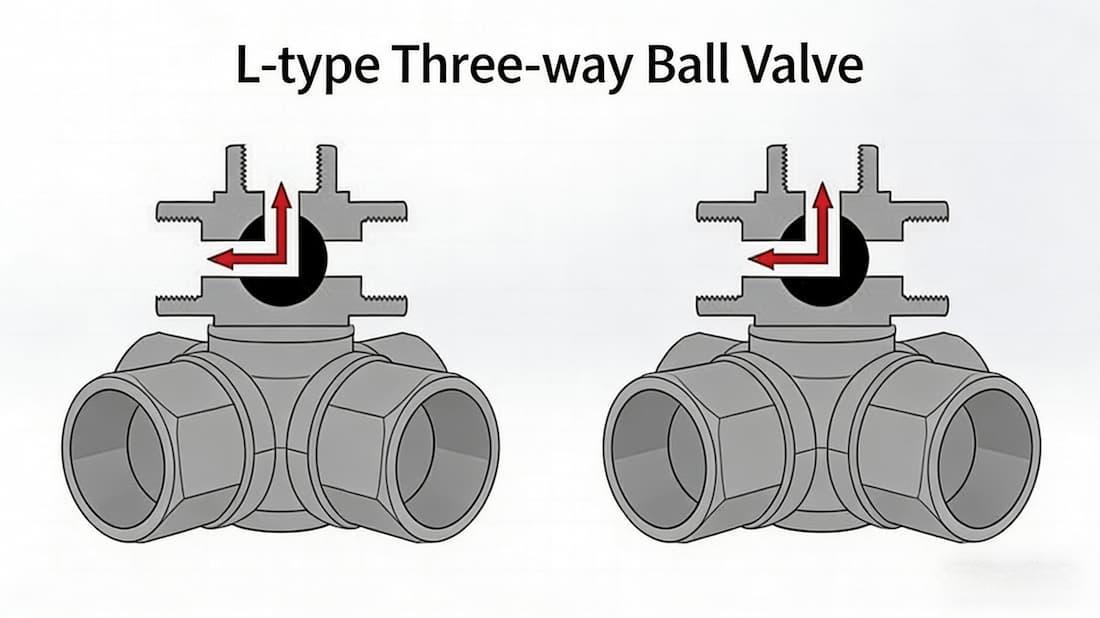
The first step in selecting the right 3-way valve is understanding the different valve types available. T-port valves offer versatile flow diversion, while L-port valves are compact and ideal for more straightforward systems. Knowing the differences and advantages of each type is crucial for your system. -
Evaluate System Demands
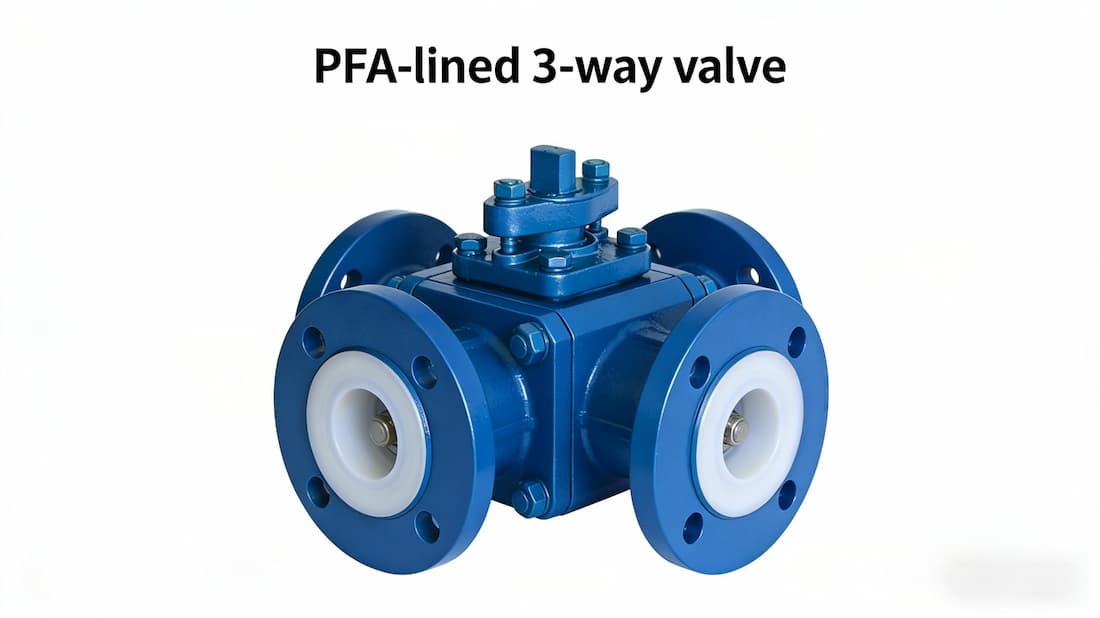
Every industrial application has specific requirements. For example, in chemical plants, PFA-lined valves are ideal due to their chemical resistance, while in water treatment, EPDM diaphragms are more suitable due to their flexibility and affordability. -
Consult Reputable Valve Manufacturers
Work with experienced valve manufacturers who can guide you through selecting the correct valve based on your needs. An expert will assess your system’s requirements—such as pressure, temperature, and chemical compatibility—and recommend the most appropriate solution.
Case Studies: Material Selection in Action
-
Case Study 1: Chemical Manufacturing Facility
A chemical processing plant needed a 3-way valve that could handle high temperatures and aggressive chemicals. After evaluating the plant’s needs, they opted for PFA-lined 3-way valves. The investment proved worthwhile as it reduced maintenance costs and valve failures, providing long-term performance. -
Case Study 2: Water Treatment Plant
In a water treatment plant, the team needed a solution for directing water flow at moderate pressures. They selected a L-port valve made with EPDM diaphragms and rubber linings. This combination proved to be cost-effective, delivering reliable performance without exceeding budget constraints.
Data/Scientific Analysis/Comparison
| Valve Type | Best For | Advantages | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| T-port | Multi-directional flow | Versatile, ideal for flow diversion | High |
| L-port | Compact, efficient flow | Space-saving, cost-effective | Moderate |
| Ball Valve | General flow control | Durable, reliable, versatile | Low |
| Butterfly Valve | Large-scale flow control | Lightweight, space-efficient | Moderate |
Data Insights: As shown in the table above, T-port valves are ideal for complex flow control, whereas L-port valves are more compact and suited for simpler systems. The choice depends on balancing cost, performance, and operational needs.
Trends/Market Insights
There is a growing demand for 3-way valves in industries such as chemical processing, water treatment, and pharmaceuticals. Innovations in materials like PTFE linings for chemical resistance and advancements in design for improved flow control are shaping the future of industrial valves. Companies are also focusing on sustainability, with an increasing interest in durable, eco-friendly valve solutions.
Style/Usage Suggestions
When choosing a 3-way valve for your industrial system, it’s essential to consider the type of media (e.g., water, chemicals, gas) and the pressure and temperature requirements. For aggressive environments, PFA-lined valves are the best choice, while stainless steel or brass valves are suitable for general applications. Ensure that you follow the manufacturer’s installation and maintenance guidelines to ensure longevity.

Conclusion & Call to Action
Choosing the right 3-way valve is crucial for optimizing your system’s performance and reducing long-term maintenance costs. By understanding the different valve types, their applications, and advantages, you can make an informed decision that maximizes efficiency. Ready to improve your system’s performance with the right valve? Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements with our experts!
FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
-
Q1: What is the difference between a T-port and L-port 3-way valve?
A1: A T-port valve allows for three flow paths and is ideal for more complex flow diversion. A L-port valve, on the other hand, offers two flow paths and is compact and cost-effective for simpler systems. -
Q2: What are the benefits of a 3-way ball valve?
A2: 3-way ball valves are durable, reliable, and ideal for controlling flow in various industrial applications. They offer quick and efficient flow control with minimal wear. -
Q3: Can 3-way valves be used in water treatment applications?
A3: Yes, 3-way valves are commonly used in water treatment to control flow direction, ensuring that the process runs smoothly without interruptions. -
Q4: How do I choose the right 3-way valve for my system?
A4: Consider the flow type, material compatibility, pressure, temperature, and your budget when selecting the right 3-way valve. -
Q5: What materials are best for 3-way valves?
A5: The best materials depend on the application. For corrosive chemicals, PFA-lined valves are ideal, while stainless steel and brass valves are suitable for general use.
References & Further Reading
-
Valve Manufacturer’s Association (VMA). (n.d.). Types of Ball Valves.
-
International Society of Automation (ISA). (2014). Valve Selection Guide. In Fundamentals of Flow Control. Wiley.
-
Parker Hannifin Corporation. (2019). How to Choose the Right 3-Way Valve.
-
Swagelok. (2015). Selecting the Right Valve for Your Application.
-
Farris Engineering. (2018). 3-Way Ball Valve Applications in Industrial Systems.