Quick Overview
Floating vs trunnion ball valve is a critical comparing in pipeline design. Although both belong to the family of industrial ball valves, their internal structures, pressure handling, and operating torque differ significantly. In this guide, Vcore Valve explains the real engineering differences, ideal applications, and practical selection tips to help you avoid overspending—or under-specifying—your valve system.
Opening Scenario: A Costly Oversight
“We selected a floating ball valve to save cost—then the actuator failed.”
After six months under high pressure, excessive torque damaged the actuator. The root cause? A trunnion-mounted design should have been used from the start.
User Pain Points
Pain Point 1: Structural Confusion
Many buyers believe the difference is only about size, not internal load distribution.
Pain Point 2: Torque Underestimation
Improper valve selection leads to high operating torque and actuator overload.
Pain Point 3: Over- or Under-Specification
Some projects overspend on trunnion valves where floating valves would suffice—others do the opposite.
Solutions & Recommendations
Solution 1: Match Valve Type to Pressure Class
Floating designs suit low-to-medium pressure; trunnion designs excel under high pressure.
Solution 2: Consider Long-Term Operation
Lower operating torque means longer actuator and seat life.
Solution 3: Consult Experienced Manufacturers
At Vcore Valve, selection is based on working pressure, DN size, and cycle frequency—not just datasheets.
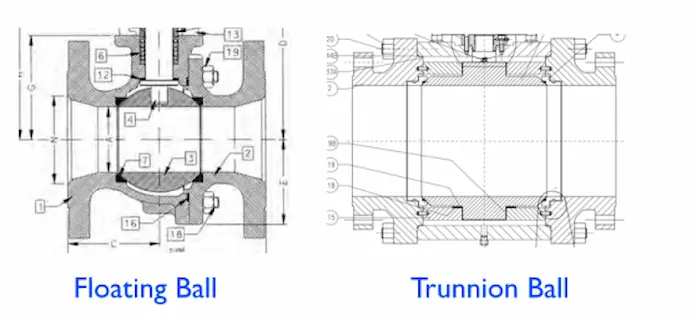
What Is a Floating Ball Valve?
A floating ball valve features a ball that is not mechanically fixed. Under pressure, the ball “floats” slightly downstream and presses against the seat to form a seal.
Key Characteristics:
-
Simple structure
-
Cost-effective design
-
Seal depends on line pressure
Typical Applications:
-
Water supply systems
-
HVAC pipelines
-
General industrial services
Floating ball valves are widely used for small to medium diameters and moderate pressure ratings.
What Is a Trunnion Ball Valve?
A trunnion ball valve has the ball mechanically anchored by trunnions at the top and bottom. The seats move instead of the ball, reducing friction and torque.
Key Characteristics:
-
Fixed ball design
-
Lower operating torque
-
Suitable for high pressure and large diameters
Typical Applications:
-
Oil and gas pipelines
-
Petrochemical plants
-
High-pressure transmission lines
Floating vs Trunnion Ball Valve: Structural Comparison
| Feature | Floating Ball Valve | Trunnion Ball Valve |
|---|---|---|
| Ball Support | Free floating | Fixed by trunnions |
| Operating Torque | Higher under pressure | Consistently low |
| Pressure Capability | Low to medium | Medium to very high |
| Valve Size Range | Small to medium DN | Medium to large DN |
| Seat Design | Soft seat dominant | Spring-loaded seats |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Case Studies & Practical Examples
Case 1: Municipal Water System
A DN80 floating ball valve provided reliable shut-off at low pressure with minimal cost.
Case 2: Natural Gas Pipeline
A DN400 trunnion ball valve reduced operating torque by over 40%, extending actuator service life.
Engineering Data & Performance Analysis
Tests show that operating torque in large floating ball valves increases exponentially with pressure. In contrast, trunnion ball valves maintain stable torque levels due to their fixed-ball design.
For high-cycle operations, trunnion designs significantly reduce seat wear and stem stress.
Market Trends & Industry Insights
-
Growing demand for trunnion ball valves in LNG and hydrogen pipelines
-
Increased use of metal-seated designs
-
Higher emphasis on automation-friendly, low-torque valves
Energy transition projects are accelerating the adoption of advanced ball valve technologies.
Style & Usage Recommendations
Choose a floating ball valve if:
-
Pressure is moderate
-
Budget is limited
-
Valve size is small
Choose a trunnion ball valve if:
-
Pressure is high
-
DN size exceeds standard limits
-
Automated operation is required
Rule of Thumb: If torque calculation raises doubts, go trunnion.
Conclusion
The difference between a floating and trunnion ball valve is not cosmetic—it directly affects safety, cost, and reliability. Selecting the right design ensures smooth operation and long service life.
👉 Contact Vcore Valve for expert guidance on ball valve selection tailored to your project conditions.
FAQs
Q1: Is a trunnion ball valve always better?
No. It is better for high pressure and large sizes, but unnecessary for small systems.
Q2: Why does a floating ball valve have higher torque?
Because the ball presses directly against the seat under pressure.
Q3: Are trunnion ball valves more expensive?
Yes, due to complex structure and additional components.
Q4: Can floating ball valves be automated?
Yes, but actuator sizing must consider higher torque.
Q5: Which valve lasts longer?
Trunnion ball valves typically offer longer seat and stem life.
Q6: Does Vcore Valve manufacture both types?
Yes, with customised materials and pressure classes.
References
-
API Specification 6D – Pipeline and Piping Valves
American Petroleum Institute.
Authoritative standard covering design, testing, and application of floating and trunnion ball valves. -
ISO 17292:2017 – Metal Ball Valves for Petroleum, Petrochemical and Allied Industries
International Organization for Standardization.
Defines structural and performance requirements for industrial ball valves. -
ASME B16.34 – Valves – Flanged, Threaded, and Welding End
American Society of Mechanical Engineers.
Widely used reference for pressure-temperature ratings and material selection. -
Engineering Toolbox – Ball Valves
Comprehensive engineering reference for valve types, operating principles, and pressure behaviour. -
Valve World Magazine – Floating vs Trunnion Ball Valve Design Considerations
Industry-focused analysis on torque, sealing mechanisms, and lifecycle cost comparison. -
Flowserve Technical Handbook – Ball Valve Engineering Fundamentals
Practical insights into ball valve design, torque calculation, and application scenarios. -
Crane Co. Technical Paper – Valve Selection for High-Pressure Pipeline Systems
Explains why trunnion-mounted ball valves are preferred in large-diameter, high-pressure pipelines. -
Vcore Valve Engineering Notes
Internal manufacturing and application experience based on real project data across oil & gas, water treatment, and industrial pipelines.